Women’s health issues can range from benign to malignant, with some conditions being more common than others. In this article, we explore several prevalent female health concerns, including vaginal infections, abnormal uterine bleeding, ovarian cysts, and breast lumps, highlighting their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Women’s health conditions, like many other diseases, can be either benign or malignant. Here are some of the most common ones:
Vaginal Infections: Almost every woman will experience a vaginal infection at least once in her lifetime. These infections come in various types and are more commonly observed in women who have sexual partners.
One type of infection is candidiasis, a fungal infection that causes severe itching and vaginal inflammation. Another type is trichomonas vaginalis, a watery infection with a fishy odor. Gardnerella infections can create a grayish layer on the vaginal mucosa.

Treatment for these infections typically includes medications and creams based on the infection type. It’s important to complete the entire treatment course to prevent recurrence. Women should also pay attention to personal hygiene and wear loose, clean, cotton underwear.
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Uterine bleeding is a broad topic. Menstrual irregularities can vary from light spotting to delays or early onset of menstruation and even heavy bleeding, with each having its own specific cause and treatment.
These bleeds can occur at various life stages, such as before puberty, during adolescence, in the reproductive years, and during menopause. Common causes include hormonal changes, birth control pills, uterine diseases, pregnancy, miscarriage, and menopause.
Abnormal bleeding can present as spotting between periods or cycles shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days. In severe cases, it might involve clotting. Identifying the cause of the bleeding is crucial.
Severe bleeding can lead to reduced red blood cells, causing weakness and fatigue. To diagnose the cause, imaging tests, hormonal tests, pregnancy tests, pap smears, or a biopsy may be needed.
Biopsy is typically done when malignancy in the uterine wall or cervix is suspected. Treatment can range from medication to surgery, or in severe cases, hysterectomy.
Ovarian Cysts: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common ovarian conditions, characterized by multiple small cysts around the ovaries. Patients often report issues like delayed menstruation, excessive hair growth, and infertility.
There is no definitive cure for ovarian cysts, but symptoms can often be controlled with medication and weight management. Most cysts are benign and resolve on their own over time. There are different types of cysts, including follicular cysts, corpus luteum cysts, dermoid cysts, adenoma cysts, and endometrioma cysts.
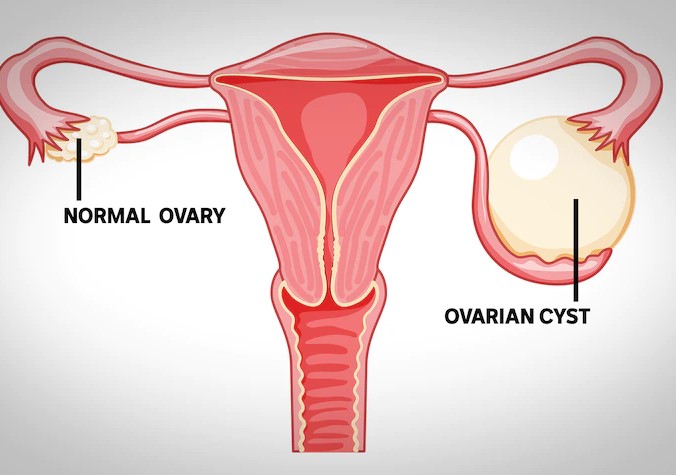
Cysts usually don’t cause symptoms, but they may lead to bloating, swelling, pelvic pain, painful intercourse, lower abdominal and back pain, nausea, and vomiting. If a cyst ruptures or twists, it can cause severe pain.
Diagnosis typically involves ultrasound, and if malignancy is suspected, a biopsy may be necessary. In cases of malignancy, removal of the cyst along with part or all of the ovary might be required.
Breast Lumps: Breast lumps often cause significant concern in women. These lumps can be of various types, including fibroadenomas, cysts, fibrocystic lumps, and malignant tumors.
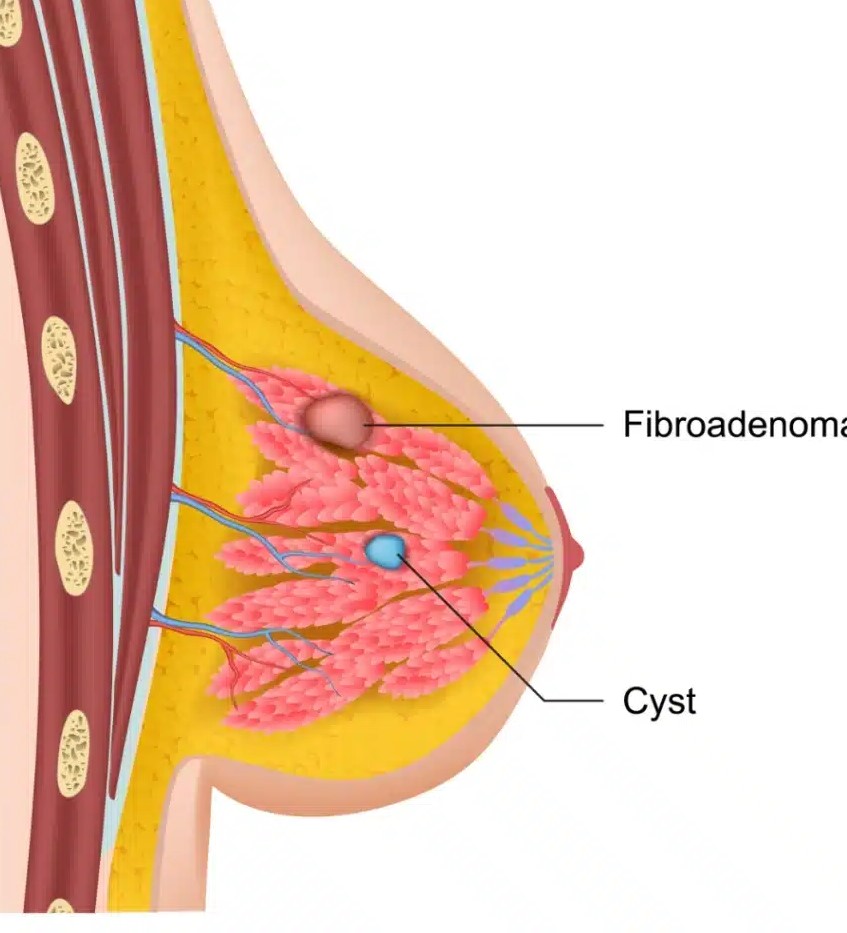
Fibrocystic lumps are one of the most common types in women and are considered a normal part of breast tissue. However, many women worry when they discover these lumps, and in some cases, cysts grow large enough to cause concern.
These lumps generally do not require treatment, but large lumps may need to be drained by a surgeon through a procedure called FNA (Fine Needle Aspiration). If the fluid appears suspicious, a biopsy might be necessary. Fibroadenomas are common in young women, typically under 25 years old, and are benign, usually requiring no surgery.
jahanbanou.ir


